Business Intelligence (Bi) Can Be Characterized as a Transformation of
Business intelligence (BI) is a technology-driven process for analyzing data and delivering actionable information that helps executives, managers and workers make informed business decisions. As office of the BI process, organizations collect data from internal Information technology systems and external sources, set up it for analysis, run queries against the information and create data visualizations, BI dashboards and reports to make the analytics results bachelor to business organization users for operational decision-making and strategic planning.
The ultimate goal of BI initiatives is to drive better business decisions that enable organizations to increase acquirement, improve operational efficiency and proceeds competitive advantages over business concern rivals. To accomplish that goal, BI incorporates a combination of analytics, data management and reporting tools, plus various methodologies for managing and analyzing data.
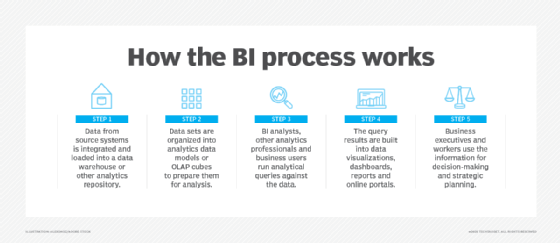
How the business concern intelligence process works
A business concern intelligence architecture includes more than only BI software. Business intelligence data is typically stored in a data warehouse built for an entire organisation or in smaller data marts that agree subsets of business organization information for private departments and business organization units, often with ties to an enterprise information warehouse. In improver, data lakes based on Hadoop clusters or other big information systems are increasingly used as repositories or landing pads for BI and analytics data, especially for log files, sensor data, text and other types of unstructured or semistructured data.
BI data can include historical information and real-time data gathered from source systems as information technology's generated, enabling BI tools to back up both strategic and tactical conclusion-making processes. Before it's used in BI applications, raw information from dissimilar source systems by and large must be integrated, consolidated and apple-pie using data integration and data quality direction tools to ensure that BI teams and business organisation users are analyzing authentic and consistent information.
From in that location, the steps in the BI process include the following:
- data preparation, in which information sets are organized and modeled for analysis;
- belittling querying of the prepared data;
- distribution of cardinal performance indicators (KPIs) and other findings to business users; and
- use of the information to aid influence and drive business decisions.
Initially, BI tools were primarily used by BI and IT professionals who ran queries and produced dashboards and reports for business users. Increasingly, however, business analysts, executives and workers are using business organisation intelligence platforms themselves, thanks to the development of self-service BI and information discovery tools. Self-service business intelligence environments enable business users to query BI data, create data visualizations and pattern dashboards on their own.
BI programs often incorporate forms of avant-garde analytics, such as data mining, predictive analytics, text mining, statistical analysis and big data analytics. A common instance is predictive modeling that enables what-if assay of different business scenarios. In most cases, though, advanced analytics projects are conducted by divide teams of information scientists, statisticians, predictive modelers and other skilled analytics professionals, while BI teams oversee more than straightforward querying and analysis of business organization information.
Why business intelligence is of import
Overall, the role of business intelligence is to meliorate an system's business organization operations through the apply of relevant data. Companies that finer employ BI tools and techniques tin can translate their collected information into valuable insights about their business concern processes and strategies. Such insights tin so be used to make better business organisation decisions that increase productivity and acquirement, leading to accelerated business growth and higher profits.
Without BI, organizations tin't readily take reward of data-driven determination-making. Instead, executives and workers are primarily left to base important business decisions on other factors, such equally accumulated knowledge, previous experiences, intuition and gut feelings. While those methods can result in proficient decisions, they're too fraught with the potential for errors and missteps because of the lack of data underpinning them.
Benefits of business organization intelligence
A successful BI program produces a variety of business organization benefits in an system. For case, BI enables C-suite executives and department managers to monitor business performance on an ongoing basis so they can act quickly when issues or opportunities arise. Analyzing client data helps brand marketing, sales and customer service efforts more constructive. Supply chain, manufacturing and distribution bottlenecks can exist detected earlier they cause financial harm. HR managers are meliorate able to monitor employee productivity, labor costs and other workforce information.
Overall, the key benefits that businesses can get from BI applications include the ability to:
- speed up and better conclusion-making;
- optimize internal business processes;
- increase operational efficiency and productivity;
- spot business organization bug that need to be addressed;
- identify emerging business and market trends;
- develop stronger business strategies;
- drive higher sales and new revenues; and
- proceeds a competitive border over rival companies.
BI initiatives also provide narrower business benefits -- amid them, making it easier for project managers to track the condition of concern projects and for organizations to gather competitive intelligence on their rivals. In addition, BI, data management and It teams themselves benefit from business intelligence, using it to clarify diverse aspects of technology and analytics operations.
Types of business intelligence tools and applications
Business intelligence combines a broad set up of data analysis applications designed to meet different information needs. Virtually are supported by both self-service BI software and traditional BI platforms. The list of BI technologies that are bachelor to organizations includes the following:
Ad hoc analysis . Also known as ad hoc querying, this is ane of the foundational elements of modernistic BI applications and a key feature of self-service BI tools. It's the process of writing and running queries to analyze specific concern issues. While ad hoc queries are typically created on the fly, they oftentimes finish upwards being run regularly, with the analytics results incorporated into dashboards and reports.
Online analytical processing (OLAP). I of the early BI technologies, OLAP tools enable users to clarify data along multiple dimensions, which is particularly suited to complex queries and calculations. In the past, the data had to be extracted from a data warehouse and stored in multidimensional OLAP cubes, but it's increasingly possible to run OLAP analyses direct against columnar databases.
Mobile BI . Mobile business intelligence makes BI applications and dashboards available on smartphones and tablets. Often used more to view data than to analyze information technology, mobile BI tools typically are designed with an emphasis on ease of utilise. For example, mobile dashboards may only display two or three data visualizations and KPIs so they can easily be viewed on a device's screen.
Real-fourth dimension BI . In real-time BI applications, data is analyzed as it's created, collected and processed to give users an up-to-date view of business organization operations, customer beliefs, fiscal markets and other areas of interest. The real-fourth dimension analytics process often involves streaming information and supports determination analytics uses, such as credit scoring, stock trading and targeted promotional offers.
Operational intelligence (OI). Also chosen operational BI, this is a class of real-time analytics that delivers data to managers and frontline workers in concern operations. OI applications are designed to help in operational conclusion-making and enable faster action on issues -- for case, helping telephone call center agents to resolve problems for customers and logistics managers to ease distribution bottlenecks.
Software-as-a-service BI . SaaS BI tools use cloud computing systems hosted past vendors to evangelize data assay capabilities to users in the form of a service that's typically priced on a subscription ground. Also known every bit deject BI, the SaaS option increasingly offers multi-cloud support, which enables organizations to deploy BI applications on dissimilar deject platforms to meet user needs and avoid vendor lock-in.
Open source BI (OSBI). Business intelligence software that is open source typically includes two versions: a community edition that tin can be used gratuitous of charge and a subscription-based commercial release with technical support by the vendor. BI teams can as well access the source code for development uses. In improver, some vendors of proprietary BI tools offer free editions, primarily for individual users.
Embedded BI . Embedded business intelligence tools put BI and information visualization functionality straight into concern applications. That enables business users to analyze data within the applications they use to do their job. Embedded analytics features are most commonly incorporated by application software vendors, but corporate software developers tin can also include them in homegrown applications.
Collaborative BI . This is more of a procedure than a specific engineering. Information technology involves the combination of BI applications and collaboration tools to enable dissimilar users to work together on data analysis and share information with one some other. For case, users tin annotate BI data and analytics results with comments, questions and highlighting via the apply of online chat and discussion tools.
Location intelligence (LI). This is a specialized class of BI that enables users to analyze location and geospatial data, with map-based information visualization functionality incorporated. Location intelligence offers insights on geographic elements in business data and operations. Potential uses include site selection for retail stores and corporate facilities, location-based marketing and logistics management.
Business intelligence vendors and market
Self-service BI and data visualization tools have go the standard for modern BI software. Tableau, Qlik and Spotfire, which is now part of Tibco Software, took the lead in developing self-service technology early on and became prominent competitors in the BI market by 2010. Most vendors of traditional BI query and reporting tools have followed in their path since then. At present, virtually every major BI tool incorporates self-service features, such as visual data discovery and advertising hoc querying.
In addition, modern BI platforms typically include:
- data visualization software for designing charts and other infographics to show data in an easy-to-grasp way;
- tools for building BI dashboards, reports and performance scorecards that display visualized data on KPIs and other business metrics;
- data storytelling features for combining visualizations and text in presentations for business users; and
- usage monitoring, functioning optimization, security controls and other functions for managing BI deployments.
BI tools are available from dozens of vendors overall. Major IT vendors that offering BI software include IBM, Microsoft, Oracle, SAP, SAS and Salesforce, which bought Tableau in 2022 and besides sells its ain tools developed before the conquering. Google is also in the BI market through its Looker unit, acquired in 2020. Other notable BI vendors include Alteryx, Domo, GoodData, Infor Birst, Information Builders, Logi Analytics, MicroStrategy, Pyramid Analytics, Sisense, ThoughtSpot and Yellowfin.
While full-featured BI platforms are the most widely used business intelligence technology, the BI market too includes other product categories. Some vendors offer tools specifically for embedded BI uses; examples include GoodData and Logi Analytics. Companies like Looker, Sisense and ThoughtSpot target complex and curated data analysis applications. Diverse dashboard and data visualization specialists focus on those parts of the BI procedure; other vendors specialize in information storytelling tools.
Examples of business intelligence use cases
In general terms, enterprise BI use cases include:
- monitoring business performance or other types of metrics;
- supporting decision-making and strategic planning;
- evaluating and improving business processes;
- giving operational workers useful information about customers, equipment, supply chains and other elements of business organisation operations; and
- detecting trends, patterns and relationships in data.
Specific employ cases and BI applications vary from industry to industry. For example, fiscal services firms and insurers use BI for take chances analysis during the loan and policy approval processes and to place boosted products to offer to existing customers based on their current portfolios. BI helps retailers with marketing campaign management, promotional planning and inventory management, while manufacturers rely on BI for both historical and real-fourth dimension analysis of plant operations and to help them manage production planning, procurement and distribution.
Airlines and hotel bondage are big users of BI for things such as tracking flight chapters and room occupancy rates, setting and adjusting prices, and scheduling workers. In healthcare organizations, BI and analytics aid in the diagnosis of diseases and other medical conditions and in efforts to improve patient care and outcomes. Universities and school systems tap BI to monitor overall student operation metrics and identify individuals who might demand assistance, among other applications.
Business intelligence for big information
BI platforms are increasingly being used as front-terminate interfaces for big data systems that contain a combination of structured, unstructured and semistructured data. Modernistic BI software typically offers flexible connectivity options, enabling information technology to connect to a range of data sources. This, along with the relatively simple user interface (UI) in most BI tools, makes it a good fit for big data architectures.
Users of BI tools tin access Hadoop and Spark systems, NoSQL databases and other big data platforms, in addition to conventional data warehouses, and get a unified view of the diverse data stored in them. That enables a broad number of potential users to get involved in analyzing sets of big data, instead of highly skilled data scientists being the only ones with visibility into the data.
Alternatively, big information systems serve as staging areas for raw data that later is filtered and refined and then loaded into a information warehouse for analysis by BI users.
Business intelligence trends
In add-on to BI managers, business intelligence teams by and large include a mix of BI architects, BI developers, BI analysts and BI specialists who piece of work closely with data architects, data engineers and other data direction professionals. Business analysts and other end users are besides frequently included in the BI development procedure to represent the business organization side and make sure its needs are met.
To help with that, a growing number of organizations are replacing traditional waterfall development with Agile BI and data warehousing approaches that utilize Agile software development techniques to break up BI projects into small chunks and deliver new functionality on an incremental and iterative footing. Doing so enables companies to put BI features into use more rapidly and to refine or modify development plans every bit business organisation needs change or new requirements emerge.
Other notable trends in the BI market include the following:
- The proliferation of augmented analytics technologies . BI tools increasingly offer natural linguistic communication querying capabilities as an alternative to writing queries in SQL or another programming linguistic communication, plus AI and machine learning algorithms that help users discover, empathise and prepare data and create charts and other infographics.
- Low-code and no-lawmaking development. Many BI vendors are besides adding graphical tools that enable BI applications to be developed with piddling or no coding.
- Increased utilise of the deject. BI systems initially were irksome to movement to the deject, partly because data warehouses were primarily deployed in on-premises information centers. But cloud deployments of both data warehouses and BI tools are growing; in early 2020, consulting firm Gartner said most new BI spending is now for cloud-based projects.
- Efforts to improve information literacy . With self-service BI broadening the apply of business organisation intelligence tools in organizations, it's critical to ensure that new users can understand and work with information. That's prompting BI teams to include data literacy skills in user training programs. BI vendors have also launched initiatives, such every bit the Qlik-led Information Literacy Project.
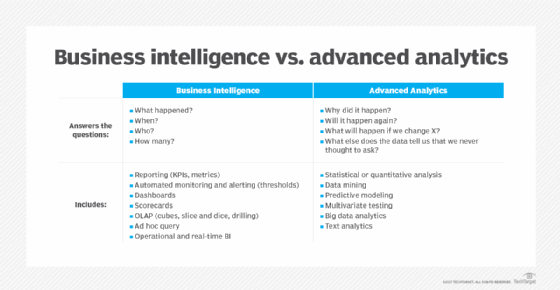
Business intelligence vs. data analytics and business organization analytics
Sporadic employ of the term concern intelligence dates dorsum to at to the lowest degree the 1860s, but consultant Howard Dresner is credited with first proposing it in 1989 every bit an umbrella phrase for applying data assay techniques to support business decision-making processes. What came to exist known as BI tools evolved from earlier, often mainframe-based analytics technologies, such as determination support systems and executive information systems that were primarily used by business executives.
Business intelligence is sometimes used interchangeably with business analytics. In other cases, business analytics is used either more than narrowly to refer to avant-garde analytics or more than broadly to include both that and BI. Meanwhile, data analytics is primarily an umbrella term that encompasses all forms of BI and analytics applications. That includes the main types of data assay: descriptive analytics, which is typically what BI provides; predictive analytics, which models future behavior and outcomes; and prescriptive analytics, which recommends business organisation actions.
Source: https://searchbusinessanalytics.techtarget.com/definition/business-intelligence-BI
0 Response to "Business Intelligence (Bi) Can Be Characterized as a Transformation of"
Post a Comment